Technology
Moving past the limitations of current CAR T approaches.
Understanding the significant unmet need.
CD19 CAR T-cell eligible patients in U.S.
It is estimated that only 20—40%
of eligible patients receive CAR T therapy1-4
Only 30—40%
of those who receive autologous CD19 CAR T therapy have durable response at 6 months5-9
Technical, operational, and access challenges
Limited manufacturing capacity
Poor status of patients’ immune cells
Manufacturing failures and extended vein-to-vein time
Limited access outside of select certified treatment centers
Unmet medical need
Vein-to-vein time of 3–6 weeks leads to bridging therapy and/or disease progression or death
60–80% of CAR T failures occur in the first three months
Most patients are hospitalized after outpatient treatment of auto-CAR T
Enhanced safety and efficacy are also needed
Overcoming cell therapy limitations.
Atara is focused on using EBV T-cell biology and novel CAR technologies to meet the current limitations of autologous and other allogeneic CAR approaches head-on.
Can be created in large quantities from healthy donors.
Can be manufactured and stored in advance of patient need for rapid treatment that may lead to shorter time to treatment, less need for bridging therapies, and better outcomes.
Can potentially expand CAR T treatment usage beyond authorized treatment centers to substantially increase equitable patient access to treatment centers.
May offer an opportunity to re-dose, which could reduce the risk of relapse.
Looking to the future of T-cell therapy.
EBV-sensitized TCR
- The native T-cell receptor (TCR) is a key survival signal for T cells.
- The TCR is essential for longevity of response.
Matched MHC
- Partial HLA matching helps minimize the risk of graft vs. host disease (GvHD).
- This removes the need for genomic editing or stealth approaches.
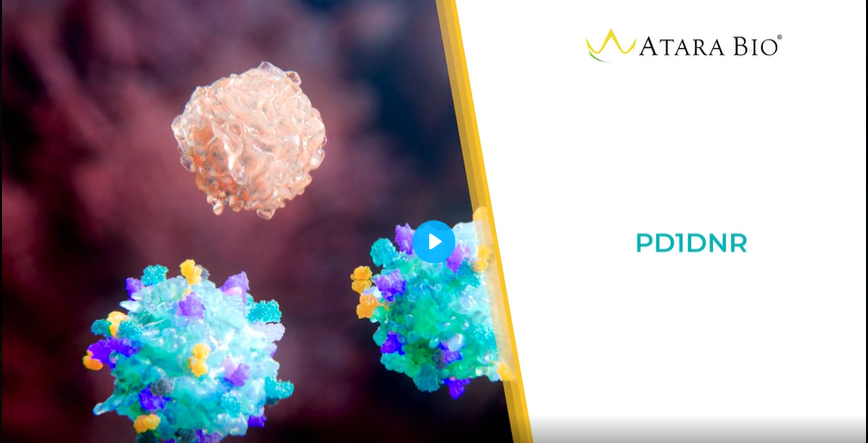
PD-1 DNR
- For solid tumors, expression of PD-1 DNR may help protect against cell exhaustion and the immunosuppressive effects of PD-1.
Binding domain
- ScFv antibody generation results in optimized affinity for the therapeutic index.
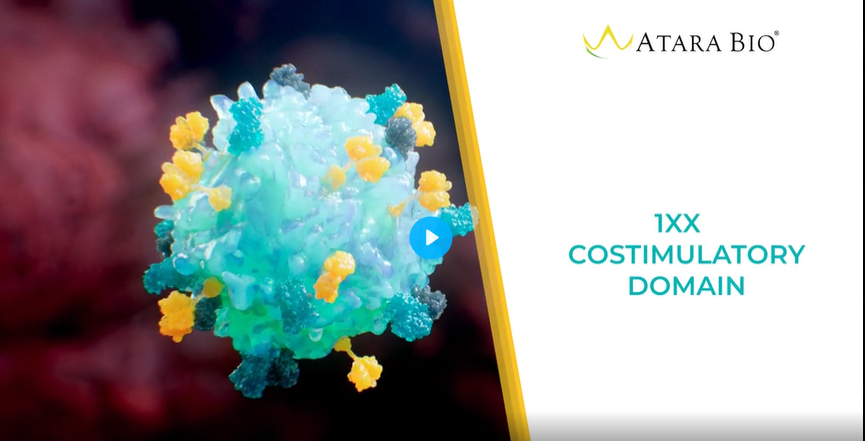
Novel 1XX costimulatory domain
- Modulates T cell differentiation and exhaustion to extend functional persistence without eliminating or compromising potency.
Memory phenotype
- A less-differentiated T cell phenotype favors expansion in the patient’s body, as opposed to during manufacturing.
- This is clinically correlated to improved durability and response.
Want to see these features at work?
See our EBV CAR T cells in action.
Discover our portfolio.
References
1Kourelis T., et al. Ethical challenges with CAR T slot allocation with idecabtagene vicleucel manufacturing access. J Clin Oncol 40, 2022.
2Geethakumari, et al. Current Hematological Malignancy Reports, 2021.
3O’Rourke K. ASCO releases guideline on CAR T-cell therapy. Cancer. 2022.
4Albendea, et al. Frontiers. 2023.
5Neelapu, S. S., et al. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:2531–2544.
6Schuster, S. J., et al. N Engl J Med. 2018; 380:45–56.
7Abramson, J. S., et al. Lancet. 2020; 396:839–852.
8Chong E. A., et al. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:673–674.
9Locke F. L., et al. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:31–42.